자유단조(自由鍛造; open die forging )
Open die forging involves the shaping of heated metal parts between a top die attached to a ram and
a bottom die attached to a hammer anvil or press bed. Metal parts are worked above their recrystallization
temperatures-ranging from 1900°F to 2400°F for steel-and gradually shaped into the desired configuration
through the skillful hammering or pressing of the work piece.
While impression or closed die forging confines the metal in dies, open die forging is distinguished by the fact
that the metal is never completely confined or restrained in the dies. Most open die forgings are produced on
flat dies. However, round swaging dies, V-dies, mandrels, pins and loose tools are also used depending on the
desired part configuration and its size.
Although the open die forging process is often associated with larger, simpler-shaped parts such as bars, blanks,
rings, hollows or spindles, in fact it can be considered the ultimate option in "custom-designed" metal components.
High-strength, long-life parts optimized in terms of both mechanical properties and structural integrity are today
produced in sizes that range from a few pounds to hundreds of tons in weight. In addition, advanced forge shops
now offer shapes that were never before thought capable of being produced by the open die forging process.
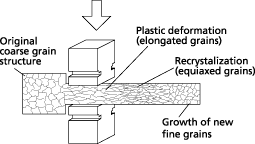 How the open die forging process affects the crystal structure. How the open die forging process affects the crystal structure.
|
|
1. The Seamless Rolled Ring Forging Process
1-1. Producing a ring "preform" by the open die forging process:
|
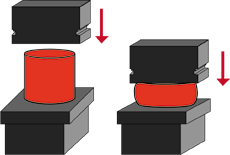 |
Starting stock cut to size by weight is first rounded, then upset to achieve
structural integrity and directional grain flow. |
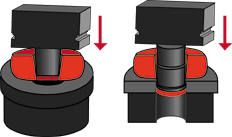 |
Work piece is punched, then pierced to achieve starting "donut" shape needed
for ring rolling process. |
 |
Completed preform ready for placement on ring mill for rolling. |
1-2. Rolled ring forging process:
|
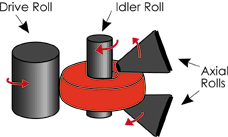 |
Ring rolling process begins with the idler roll applying pressure to
the preform against the drive roll. |
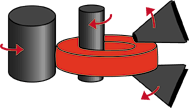 |
Ring diameters are increased as the continuous pressure reduces the wall thickness.
The axial rolls control the height of the ring as it is being rolled. |
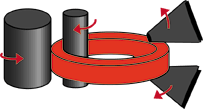 |
The process continues until the desired size is achieved. |
2. Steps to produce a typical spindle-shaped part
|
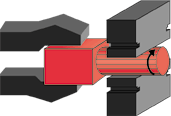 |
Rough forging a heated billet between flat dies to the
maximum diameter dimension. |
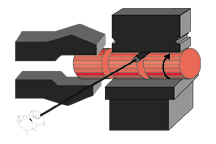 |
A "fuller" tool marks the starting "step" locations on the fully rounded workpiece. |
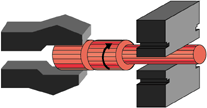 |
Forging or "drawing" down the first step to size. |
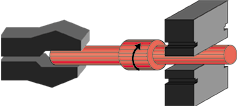 |
The second step is drawn down to size. Note how the part
elongates with each process step as the material is being displaced. |
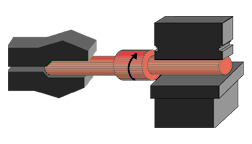 |
"Planishing" the rough forging for a smoother surface
finish and to keep stock allowance to a minimum. |