|
A schematic presentation of the rolling process, in which the thickness of the metal is reduced as it passes
through the rolls, is shown in illus. a. The speed at which the metal moves during rolling changes, as shown
in illus. b, to keep the volume rate of flow constant throughout the roll gap. Hence, as the thickness decreases,
the velocity increases; however, the surface speed of a point on the roll is constant, and there is therefore
relative sliding between the roll and the strip. The normal pressure distribution on the roll and hence on
the strip is of the form shown in illus. c. Because of its particular shape this pressure distribution is
known as the friction hill.
A great variety of roll arrangements and equipment are used in rolling. The proper reduction per pass in
rolling depends on the type of material and other factors; for soft, nonferrous metals, reductions are usually
high, while for high-strength alloys they are small. Requirements for roll materials are mainly strength and
resistance to wear. Common roll materials are cast iron, cast steel, and forged steel.
|
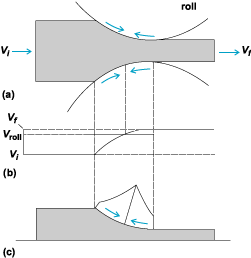
The rolling process, (a) direction of friction forces in the roll gap. (b) velocity distribution,
(c) normal pressure acting on the strip in the roll gap. Vi = initial velocity, Vf = final velocity,
Vroll = velocity during rolling operation.
|